Pituitary ,Thyroid and parathyroid
The pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is a small gland beneath the brain. It is divided into an anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) and a posterior lobe (neurohypophysis). . s


The anterior pituitary produces six hormones, including growth hormone (somatotropin), which promotes bone growth and affects various tissues. The other hormones regulate the activity of different glands, such as the thyroid, adrenal glands, gonads, and mammary glands. The suffix"-tropin" signifies a hormone that influences another gland, while the adjective form "-tropic" is used in terms like adrenocorticotropic. m

The posterior pituitary releases two hormones, produced in the hypothalamus, which are stored until needed. One of these hormones, antidiuretic hormone (ADH), acts on the kidneys to conserve water and promotes blood vessel constriction, both of which help to increase blood pressure.j
Oxytocin stimulates uterine contractions and promotes milk “letdown” in the breasts during lactation. l
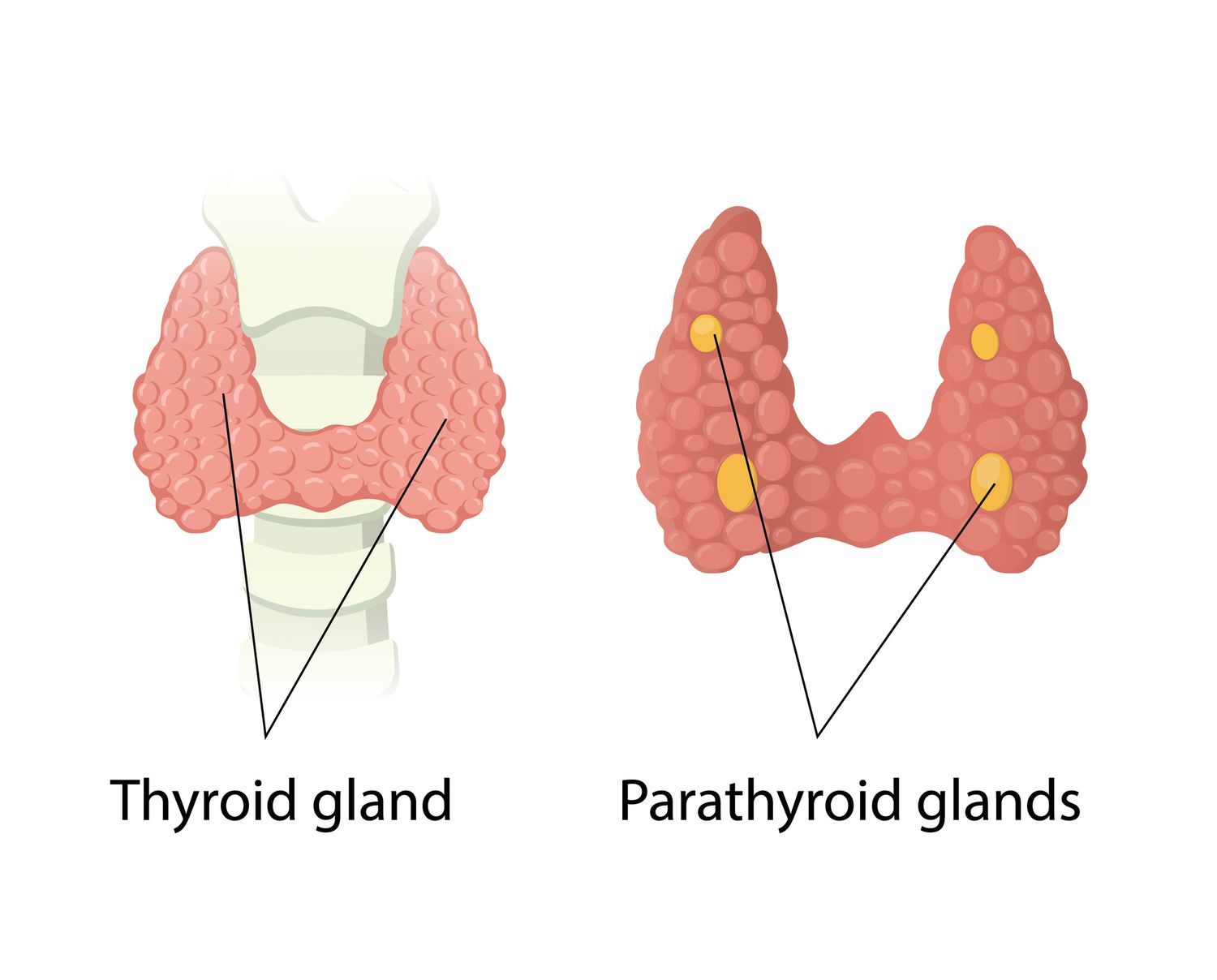
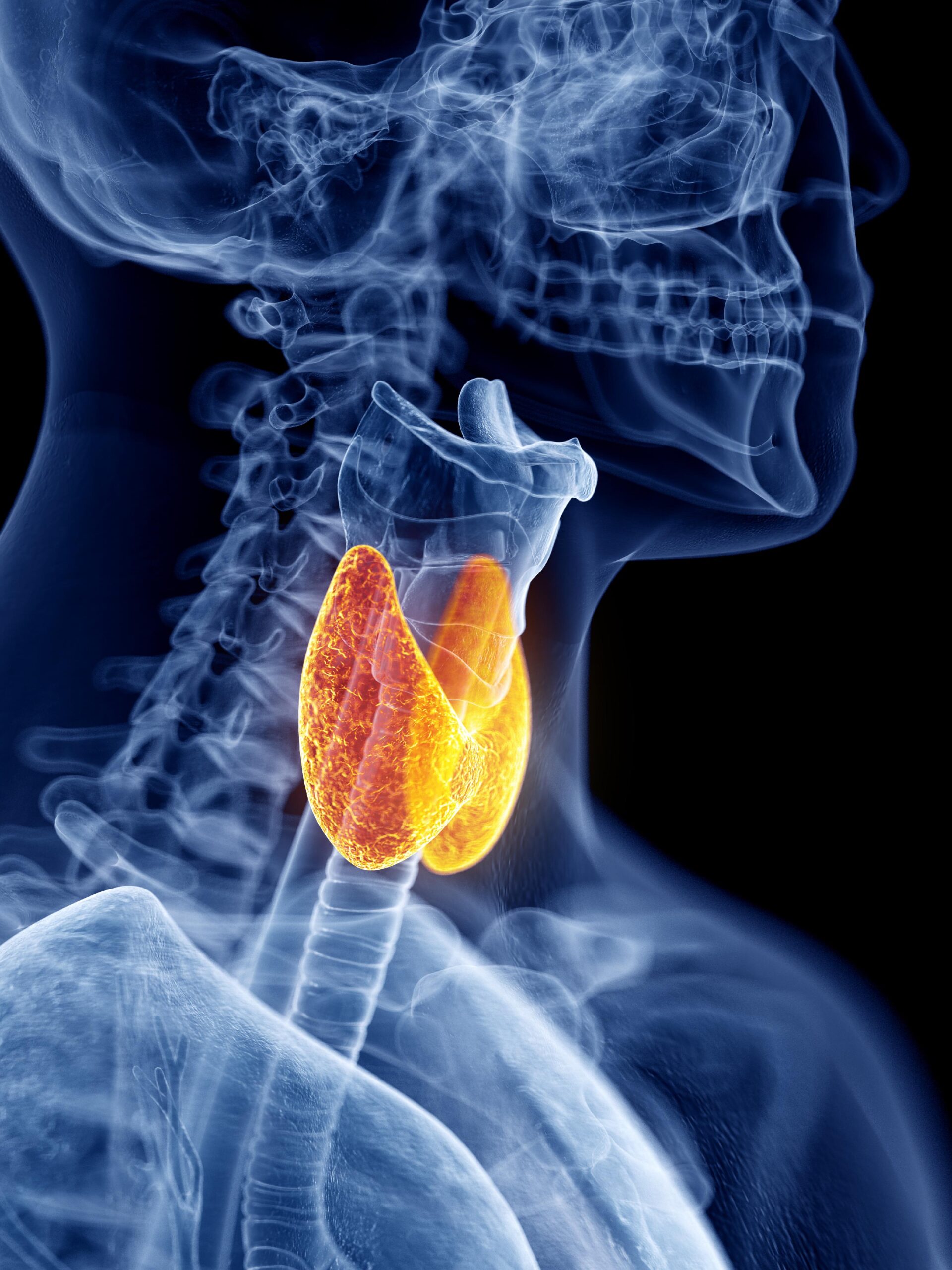
The thyroid gland consists of two lobes on either side of the larynx and upper trachea. The lobes are connected by a narrow band (isthmus). The thyroid secretes a mixture of hormones, mainly thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Because thyroid hormones contain iodine, laboratories can measure these hormones and study thyroid gland activity by following iodine levels. Most thyroid hormone in the blood is bound to protein, primarily thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG). c
On the posterior surface of the thyroid are four to six tiny parathyroid glands that affect calcium metabolism. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) regulates calcium exchange between the blood and bones. It increases the blood level of calcium when needed. m