Other Glands
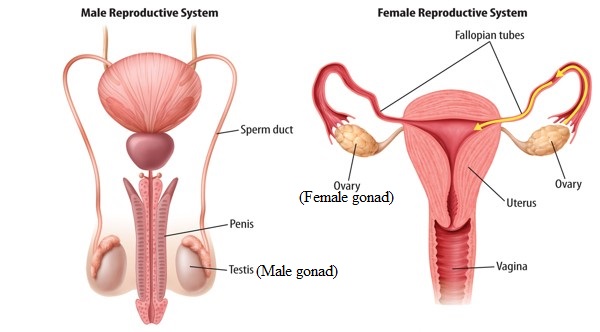
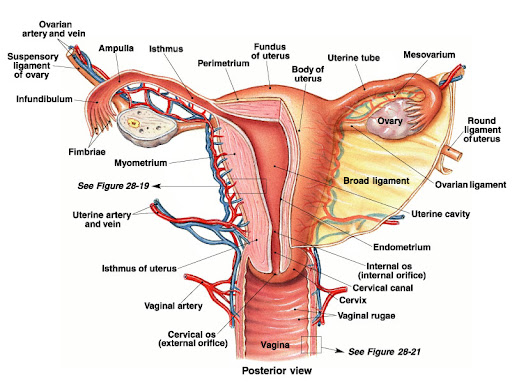
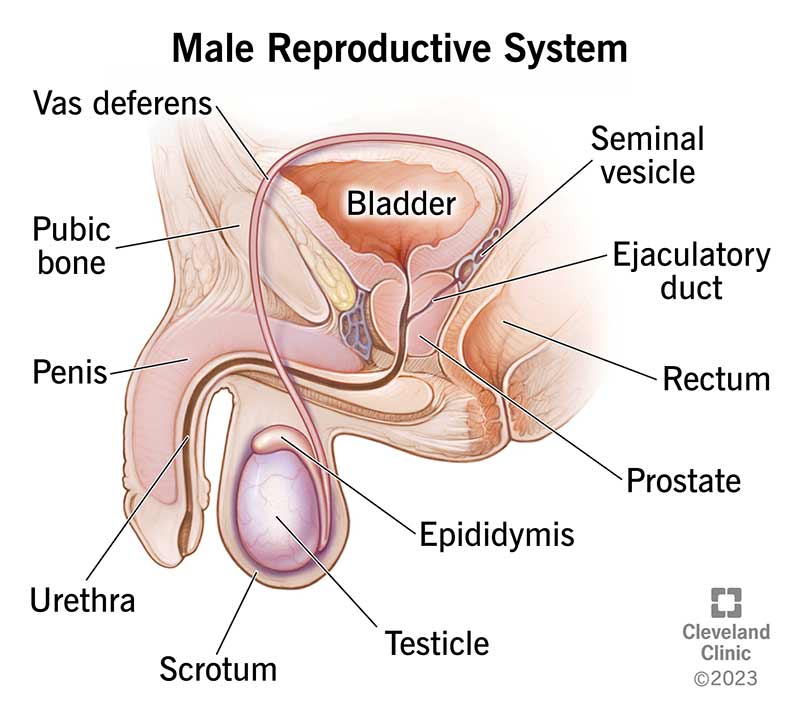
The gonads, testes , and ovaries, are also included because they secrete hormones in addition to producing the sex cells. s
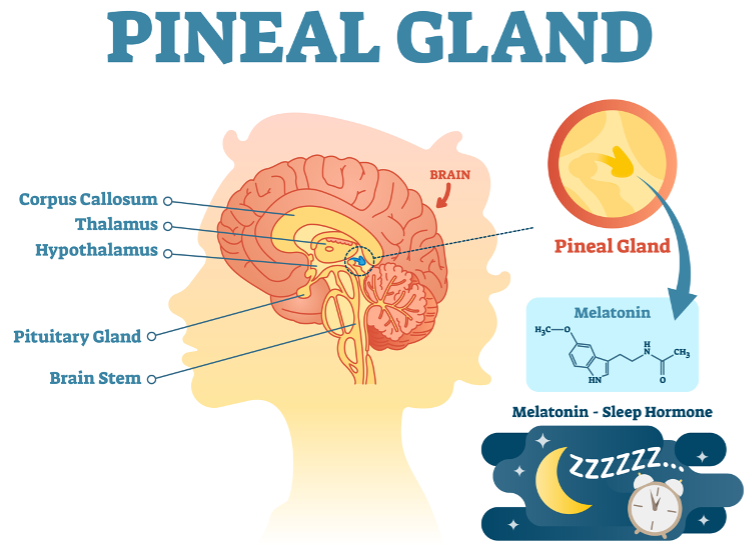
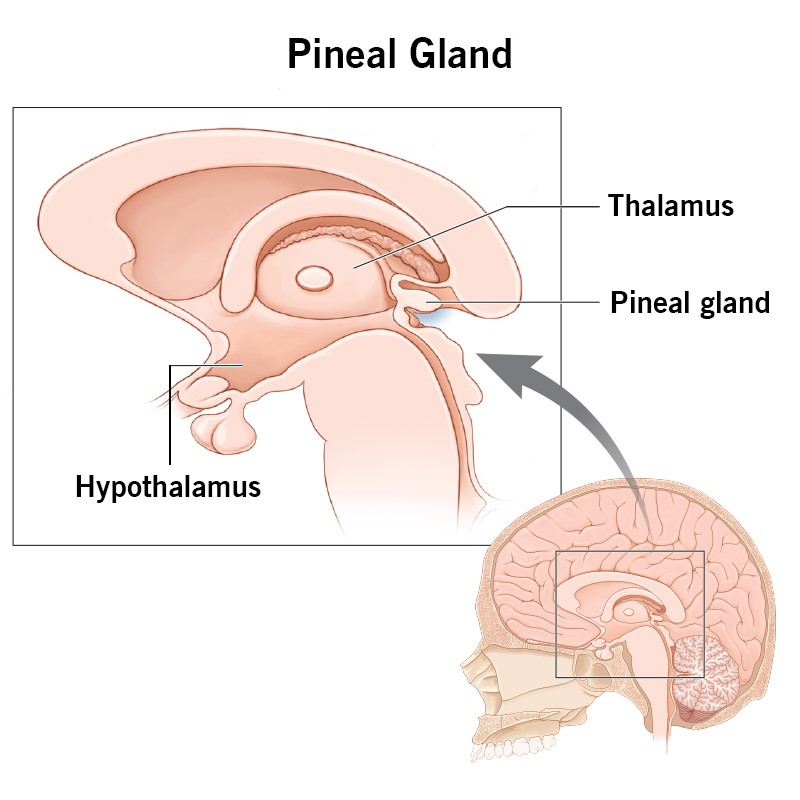
* Pineal *
The pineal gland is a small gland in the brain. It regulates mood, daily rhythms, and sexual development in response to environmental light. Its hormone is melatonin, which some people take to help regulate sleep–wake cycles when they travel between time zones.s
*Thymus*
The thymus, described in Chapter 10, secretes the hormone thymosin that aids in the development of the immune system’s T cells. The thymus lines in the upper chest above the heart. It is important in early years but shrinks and becomes less important in adults. a


*Prostaglandins*
Prostaglandins are a group of hormones produced by many cells. They have a variety of effects, including stimulation of uterine contractions, promotion of inflammation, and vasomotor activities. They are called prostaglandins because they were first discovered in the prostate gland.d


